
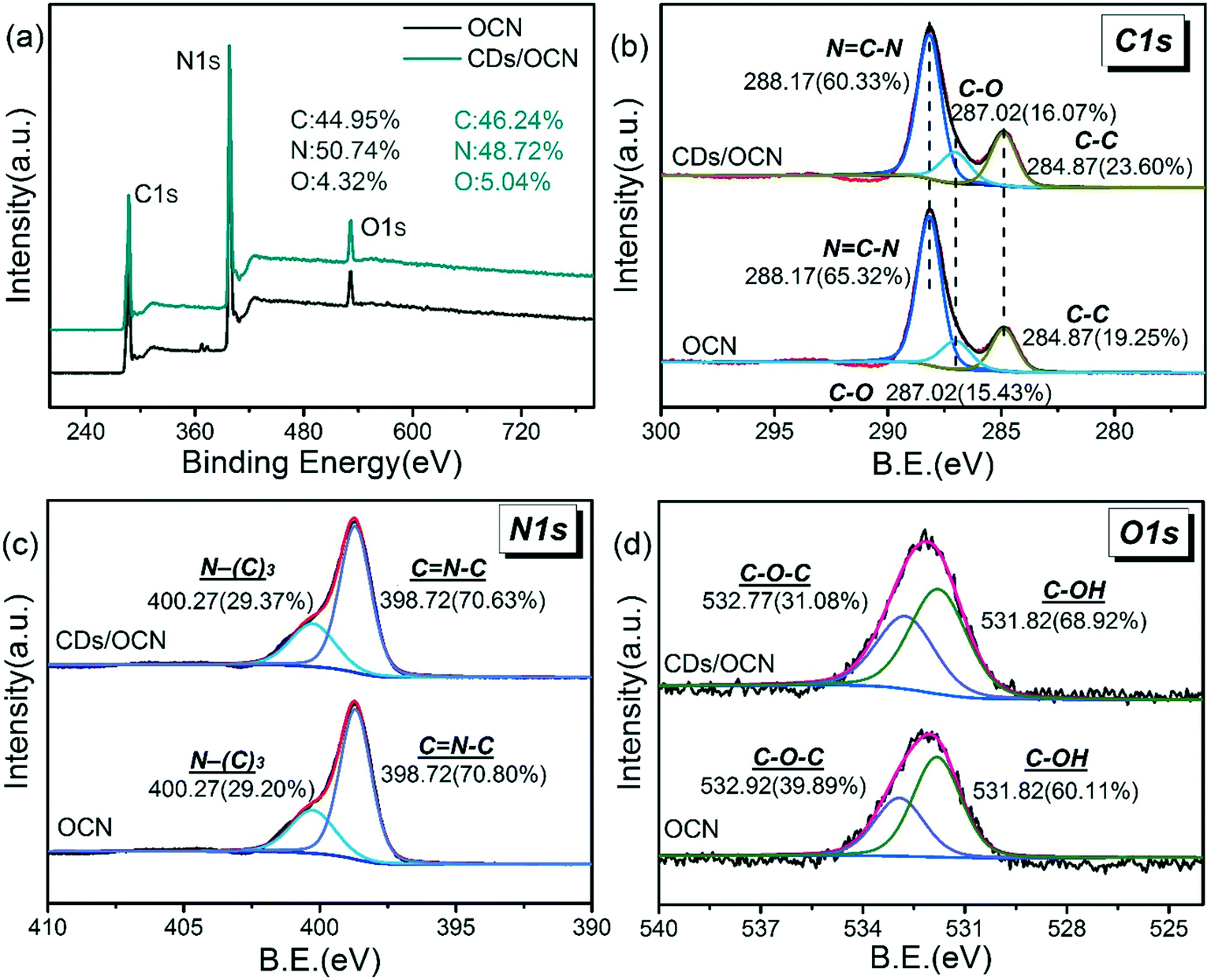
The deconvoluted C1s spectra provided detailed information about surface functional groups present on GO and GNS, including the. Oxygen is colorless, odorless, and tasteless in its gaseous form, and condenses to pale blue liquid and solid forms. XPS analysis: XPS was employed to monitor the progress of thermal and chemical reduction by observing changes in the binding energy of C1s peaks corresponding to GO and PVP-GO (Figure S2).

Accounting for one-fifth of the earth’s atmosphere, oxygen combines with most elements and is a component of thousands of organic compounds. Oxygen is critical for life on Earth, produced by plants during photosynthesis and necessary for aerobic respiration in animals. Oxygen, the "elixir of life", was discovered by Joseph Priestly and Carl Wilhem Scheele independently of each other in the 1770’s. in 35.Discoverer: Joseph Priestley/Carl Scheele In Figure 3, we see high energy resolution spectra acquired from the copper samples, A. The ability to detect and quantify this shift makes XPS such a powerful analytical technique. The small peak existing at 152.2 eV KE was referred to an Auger peak of sulfur (S) contamination by Vaughan et al. peaks in finer detail, then we see that even for the same element, the peak energy may shift depending on the surface chemistry. Since the O2s bands are closer in energy to Zr4p than with Zr4s, the overlap of O2s wave function with Zr4p is much stronger than Zr4s and can explain the non-equal shift in Auger transitions. This difference suggests a variation in the interactions between Zr-O and O-O with increasing oxygen content 30. The M 45(O)N 1(O)N 23(O) and M 45(O)N 23(O)N 23(O) are shifted of about 3.6 and 5.6 eV respectively. In order to investigate the valence band behaviour and the Auger transitions of ZrO x as a function of oxygen incorporation, several thin film samples were prepared with magnetron sputtering under different argon/oxygen atmosphere that led to various \(\frac\) = 1.3 film. Based on Auger transition corrections, an attempt to correlate the obtained results with the structural properties of ZrO x will be presented. Auger transitions involving valence bands could therefore be used as a reference for charge correction of the XPS spectra and give a better understanding of the evolution of the valence bands upon oxidation. The study of Auger, core-level and valence spectra using XPS and Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS) of the ZrO x films showed that the variation of the oxidation state do not influence the position of the O2p bands but rather the band edge of the upper valence band. This method allowed us to avoid the charging effect and to eliminate the contribution of the substrate to the measured signal. In the current investigation, the oxidation state of the films as well as their thicknesses have been controlled directly by reactive magnetron sputtering.
#URETHANE O1S XPS PEAK FULL#
This large range between reported values has been puzzling both experimentalists and theoreticians and no clear explanation has been given up-to date 19.Īlthough previous studies already addressed surface oxidation of metallic Zr under various oxygen atmosphere using photo-electron spectroscopy techniques 20, 21, 22, 23, they did not provide a full interpretation of the valence behaviour of ZrO x films. As an example, we mention that the reported band gap value of ZrO 2 varied from 3.8 to 5.8 eV for the monoclinic phase depending on the measurement techniques 15, 16, 17, 18. Indeed, the build-up of static charges at the surface for thicknesses above 5 nm can randomly shift the measured spectra 13, 14 depending on the thickness, micro-structure of the film and exposure time to X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) excitation. Deconvolution of the O1s by 4 peaks is used to determine O C and O C contributions which provide upper and lower bounds for the related C1s peaks: C O, C O and COO. XPS spectra when fitting peaks is applied for GO-2 and. To improve the self-consistency of the XPS interpretation a method is proposed based on a 7 peak C1s deconvolution, 3 C C peaks, 3 oxygenated peaks, and pi-pi transition peak. Using photo-electron spectroscopy techniques to study the properties of such an insulator is a challenging task. urethane) (PCU) polymer in order to mechanical properties improvements. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS or ESCA) curve fitting procedures, reference materials and useful notes are listed here to provide a starting point for the consistent interpretation of XPS spectra. ZrO 2 still attracts attention of other fields, thus the understanding of its electronic behaviour is crucial for the development of various technology sectors. Zirconium dioxide (ZrO 2) has been studied extensively due to its physical and chemical properties, whether in high temperature fuel cells 1, 2, 3, gas sensors 4, 5, 6, protective coating for metal anti-corrosion 7, 8, 9, or insulator on metal-oxide semiconductor devices 10, 11, 12.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
